This article contains both write-up and summary of thm Wireshark 101 Room
This room is induced by Introductory Networking Room, I think it is wonderful to use wireshark as a tool to give a further understanding of OSI Model. :)
After pass this room I think the most import part is how to filter, Im gonna extend some stuff about filter, After that, some attacks analyzed by wireshark will be presented.
0x01 Mind Map
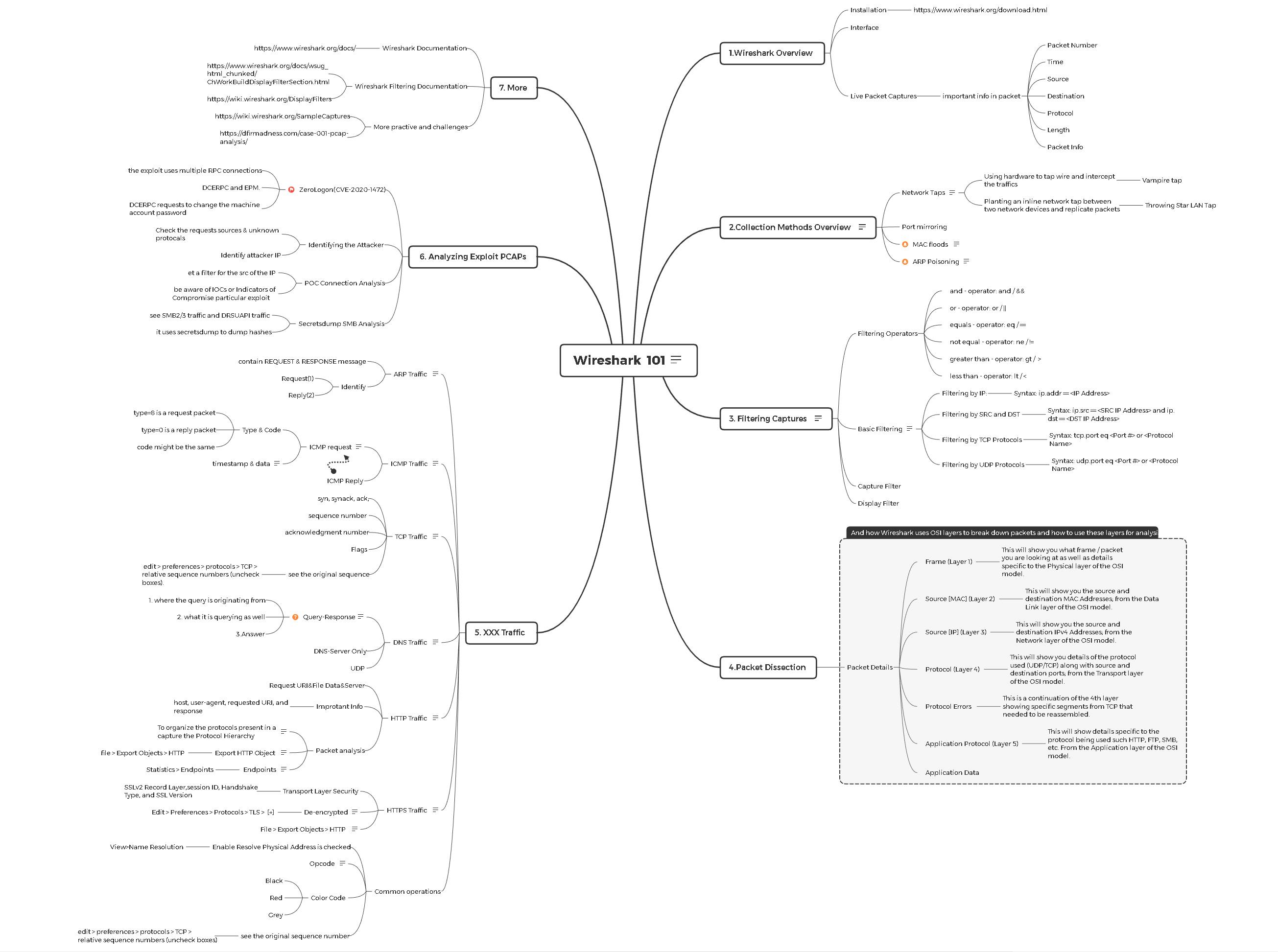
0x02 Write-up
Task 1 Introduction
No answer needed;
Task 2 Installation
No answer needed;
Task 3 Wireshark Overview
No answer needed;
Task 4 Collection Methods
No answer needed;
Task 5 Filtering Captures
No answer needed;
Task 6 Packet Dissection
No answer needed;
Task 7 ARP Traffic
1.What is the Opcode for Packet 6?
Request (1)
2.What is the source MAC Address of Packet 19?
80:fb:06:f0:45:d7
3.What 4 packets are Reply packets?
76,400,459,520
At first I completed this question by checking ARP packets one by one. So I wonder is there any way I can do in filter that could display all reply packets directly? Then I found this could be work: arp.opcode == <value>, we know reply opcode is 2, so here is the result:
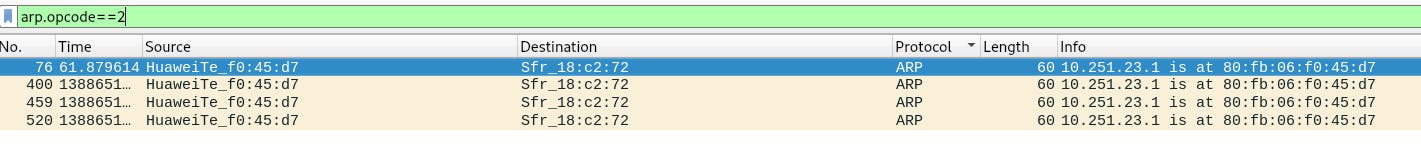
4.What IP Address is at 80:fb:06:f0:45:d7?
10.251.23.1
I still have a question here, why it is not the Sender IP address 10.251.196.1?
Task 8 ICMP Traffic
1.What is the type for packet 4?
8
2.What is the type for packet 5?
0
3.What is the timestamp for packet 12, only including month day and year?
May 30,2013
note: Wireshark bases it’s time off of your devices time zone, if your answer is wrong try one day more or less.
4.What is the full data string for packet 18?
08090a0b0c0d0e0f101112131415161718191a1b1c1d1e1f202122232425262728292a2b2c2d2e2f3031323334353637
Task 9 TCP Traffic
No answer needed;
Task 10 DNS Traffic
1.What is being queried in packet 1?
8.8.8.8.in-addr .arpa
2.What site is being queried in packet 26?
3.What is the Transaction ID for packet 26?
0x2c58
Task 11 HTTP Traffic
1.What percent of packets originate from Domain Name System?
4.7
2.What endpoint ends in .237?
145.254.160.237
3.What is the user-agent listed in packet 4?
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.6) Gecko/20040113
4.Looking at the data stream what is the full request URI from packet 18?
I felt confused here, I thought it was the content in red box, but the correct answer is in the green box.
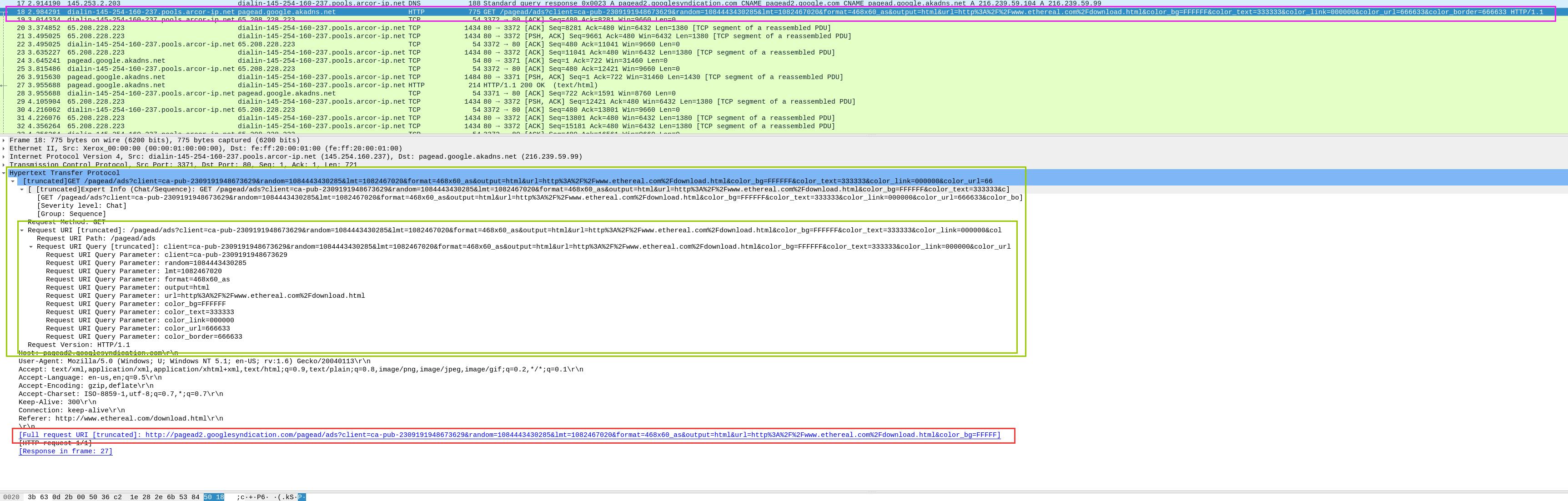
5.What domain name was requested from packet 38?
6.Looking at the data stream what is the full request URI from packet 38?
Task 12 HTTPS Traffic
1.Looking at the data stream what is the full request URI for packet 31?
2.Looking at the data stream what is the full request URI for packet 50?
3.What is the User-Agent listed in packet 50?
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux i686; fr; rv:1.8.0.2) Gecko/20060308 Firefox/1.5.0.2
In this task, what we should do is to add key file, open readme.txt in task file, then click Edit> Preferences > Protocols , and select SSL, edit:
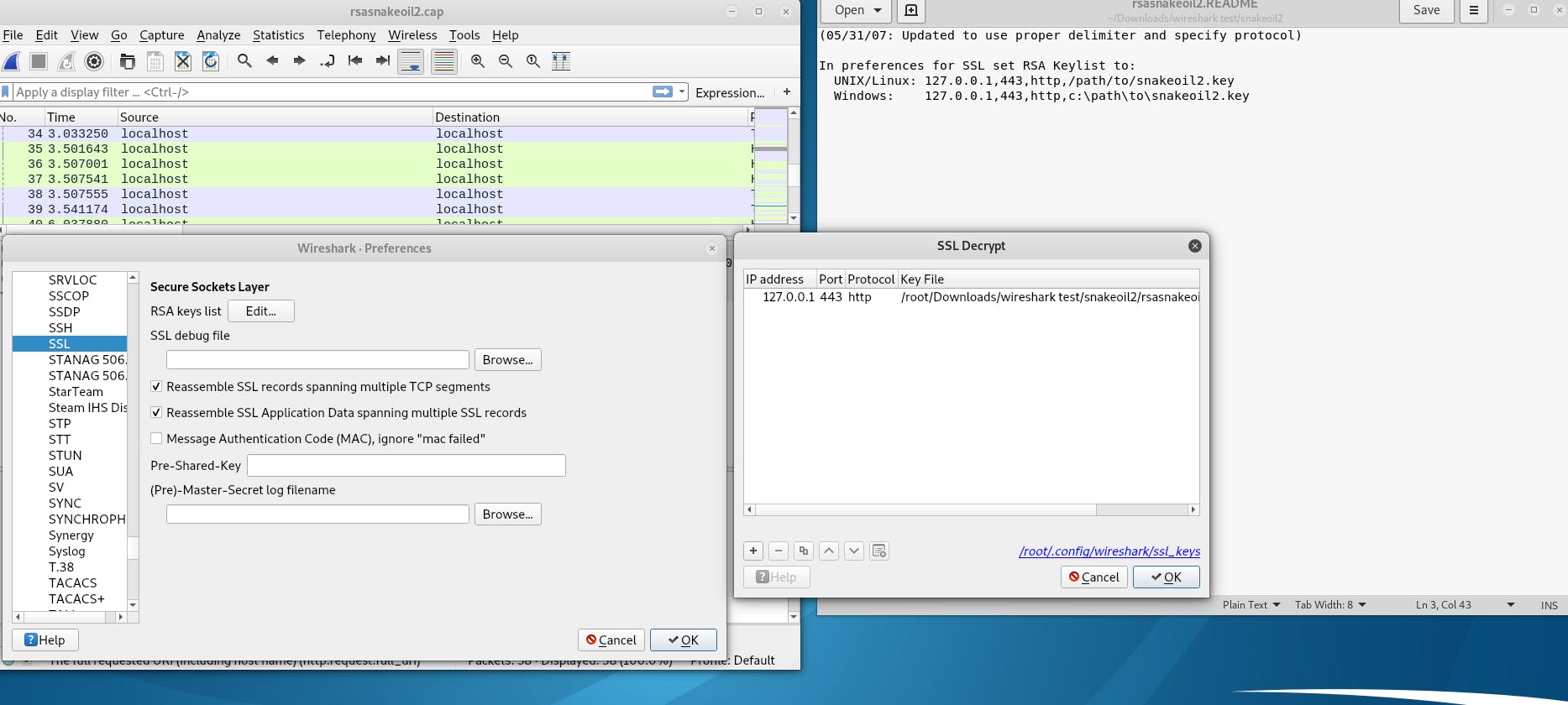
Task 13 Analyzing Exploit PCAPs
No answer needed;
Task 14 Conclusion
No answer needed;
0x03 Filter in Wireshark
When we are dealing with large amounts of data, using filter can let us focus on those useful and involved packets and speed up our analysis procedure. In summary, we are going to contact Capture Filter and Display Filter.
We can input filter statement directly in filter bar:
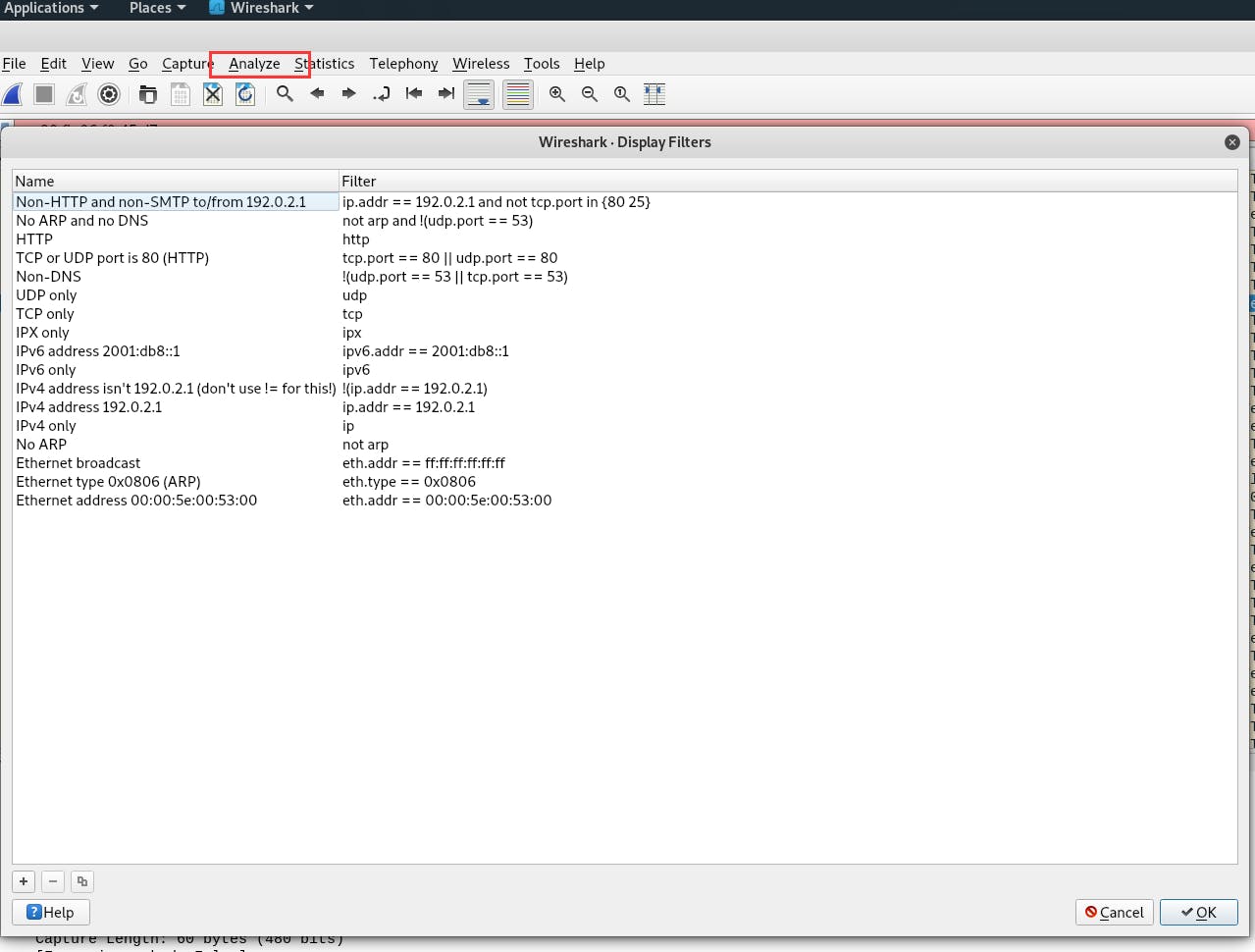
or open Display Filters in Analysis:
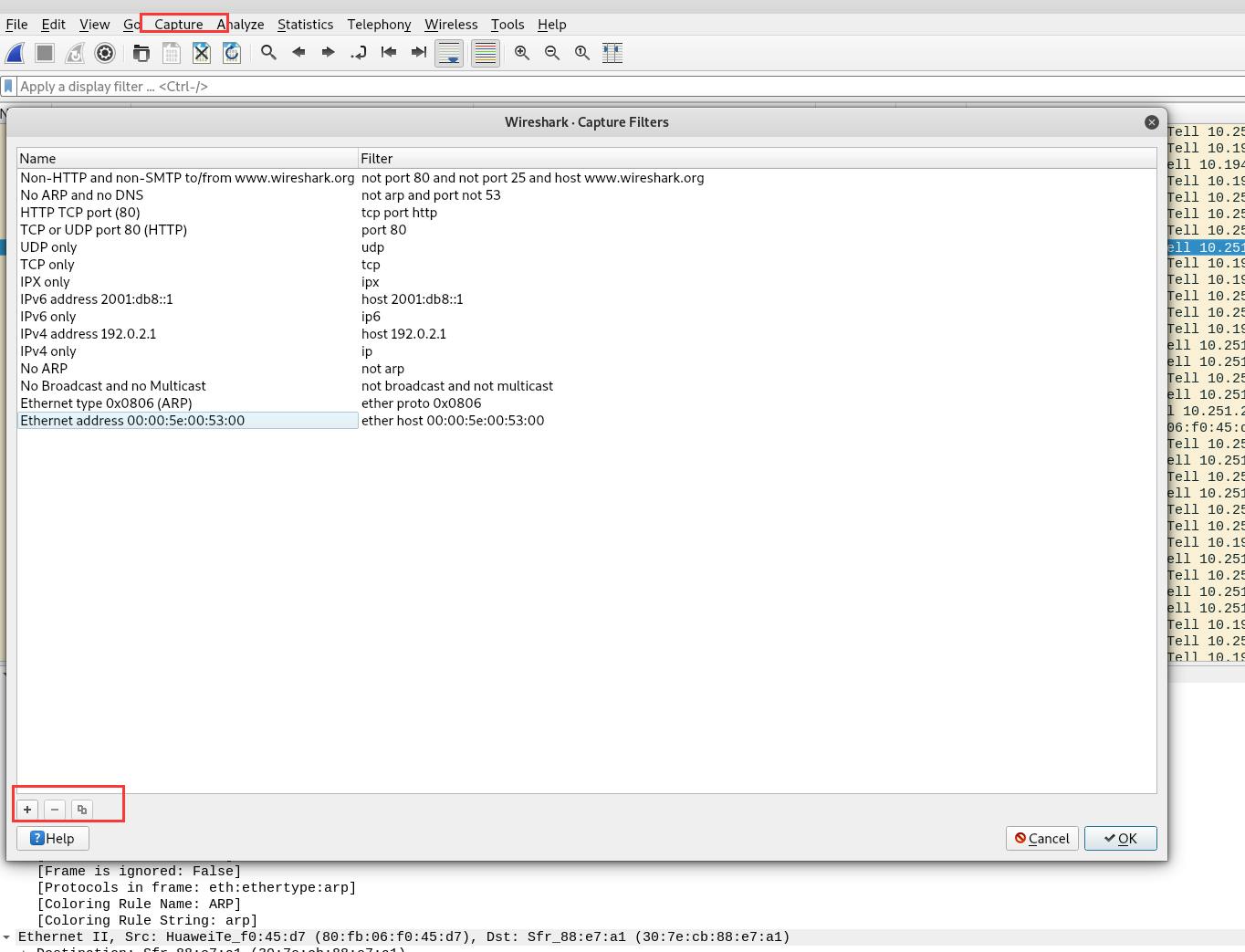
or construct filter statements by ourselves, click Capture>Capture Filters:
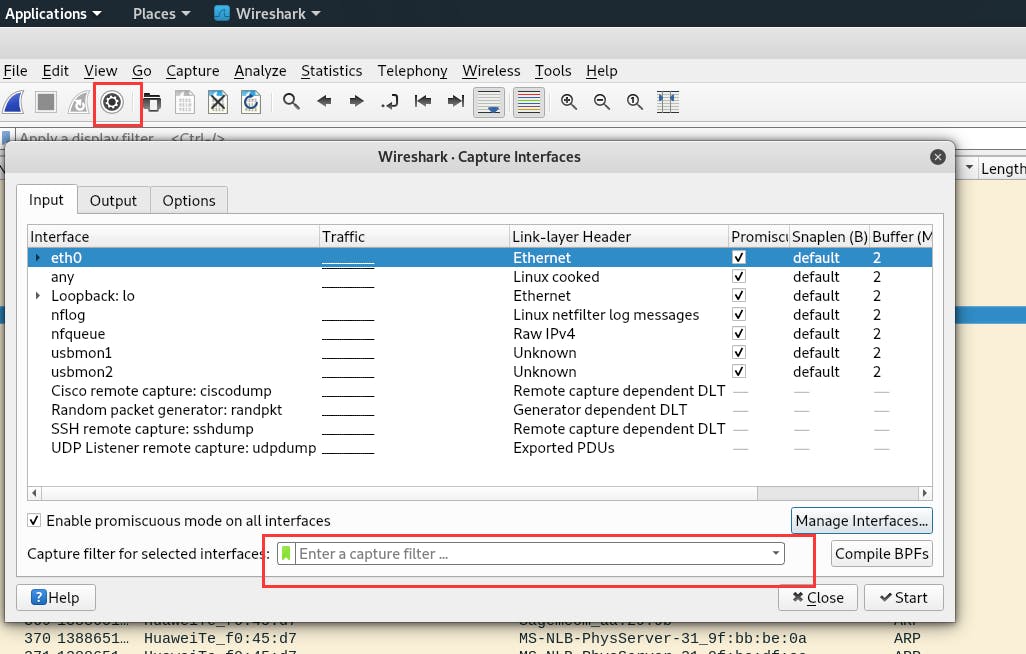
or just click this icon:
Expect these, the first we should know is BPF, Berkeley Packet Filter. Besides those filtering operators and basic filtering content, I think to know how to use the qualifier is import. There are 3 kinds of qualifier in BPF:
type: host(default), net, port
dir: src, dst, src or dst (default)
proto: ether, ip, tcp, arp ......
BPF also support it if we need do some further operation to packets. the syntax is proto [expr: size]. Here, size can be 1(default), 2 or 4. For example, we can use this expression "ip [12: 4] = 0xc0a80101" to take place " dst host 192.168.1.1"
0x04 References
Practical packet analysis (3rd edition), Chris Sanders.